Businesses today operate in a world where the growth of violence, vandalism, and theft requires ever-increasing levels of security. While commercial video security cameras have become a standard for protecting businesses, their effectiveness is limited in outdoor settings and low-light conditions. These limitations make perimeter security – the first line of defense against intrusion – particularly challenging.
Thermal imaging cameras are quickly becoming a popular choice for outdoor security applications, especially concerning perimeter security. The thermal imaging market is expected to top $4 billion by 2023. There are three reasons for the rapid, widespread adoption of this technology for security applications:
- Most businesses recognize the importance of perimeter security yet struggle to implement it effectively, often relying on a costly combination of video cameras and security patrols.
- Thermal imaging technology overcomes almost all of the challenges inherent with conventional video cameras in outdoor settings, offering much better performance, accuracy, and improved analytics combined with a significant reduction in false alarms.
- Improvements in thermal imaging technology have made thermal imaging cameras more affordable than ever, enabling businesses of all sizes to improve their security cost-effectively.
In a previous post, we discussed how thermal imaging cameras are improving fire protection. Now, we’re turning our attention to how this technology can be applied to enhance security in a wide variety of outdoor settings.
Traditional Video Cameras Vs. Thermal Imaging Cameras in Outdoor Settings
Traditional video cameras rely on visible light to capture an image and software analytics programmed to trigger an alarm when certain conditions are met. When the alarm is triggered, a video is captured and transmitted to the command and control centers for live viewing. The problem with using these cameras in outdoor settings is that many common conditions can trigger a false alarm, such as fog, heavy rain, blowing trees, and the movements of animals. There are also several conditions that can result in poor video quality. Reflections from headlights passing by the camera, glare from the sun, shadows, and low light conditions at night, can all make it difficult to determine whether the images captured on the video represent a real threat. Ultimately, visible light cameras rely on human assessment to determine if the alarm is real. And often, when deployed in outdoor settings, it’s not.
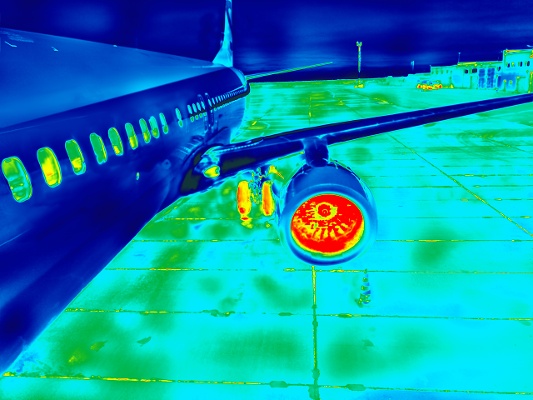
Thermal cameras overcome these issues because they rely on infrared radiation – a type of energy that, while invisible to the human eye, can be detected in the form of heat. Thermal cameras are ideal for outdoor settings because they do not require any light to operate and instead measure subtle differences in temperature, called heat signatures, to create a clear, high-resolution image that makes the potential threat easier to assess.
Thermal cameras are equipped with sensors that measure the amount of infrared radiation (or heat) emitted from objects in a given area. The measurements are then processed using specialized software to visually display the heat readings in the form of high-definition images or video. “Hot spots” or areas with higher temperatures will show up as brighter areas on the image against areas with cooler temperatures, which appear darker.
It is almost impossible to mask a heat signature, especially with the highly sensitive cameras on the market today. A thermal camera will pick up the heat signature of a person even when that person is trying to conceal his/her presence and movements. Thermal cameras can “see” through fences, bushes and other vegetation and into the shadows, making it easy to spot an intruder, even in total darkness. They can also see through haze and fog and smog, and can’t be blinded by headlights or direct sunlight.
While the initial cost of a thermal imaging camera is still a bit higher than conventional video cameras, they can usually cover the same area with fewer cameras. Unlike conventional video cameras, thermal imaging cameras have no internal lamps or infrared illuminators to replace making their maintenance minimal. Their power consumption is also minimal when compared to conventional video cameras. These features help to reduce the total cost of ownership to make the cost of a thermal imaging surveillance system closely comparable to traditional closed-circuit television systems that rely on video cameras.
Settings where Thermal Imaging Cameras can Significantly Improve Security
Thermal imaging cameras are utilized by all kinds of businesses and municipalities at every scale. Here are some of the most popular applications for thermal security cameras today:
- Construction Sites – Thermal imaging cameras can detect people entering a construction site at night when no one, other than perhaps a security guard, should be on the premises.
- Retail Locations – Thermal imaging cameras are ideal for monitoring parking lots and the back of stores at night.
- High School Football Fields – New football fields represent an enormous investment for a community. Thermal imaging cameras can help reduce vandalism on or around the field, which often occurs at night under cover of darkness.
- Rooftops – Many break-ins occur through roof access points. Thermal cameras are ideal for rooftop settings because, unlike traditional video cameras, they are effective in all weather conditions, day or night.
- Self-Storage Facilities – Break-ins at self-storage facilities are common. Thermal cameras installed to monitor the perimeter can detect movement over longer distances than traditional cameras and trigger an alarm before criminals can ever make it to a storage container door.
- Cannabis Greenhouses, Growing Facilities, and Retail Shops – The Cannabis industry is growing fast and has become a prime target for theft. Thermal security cameras around the perimeter of the property, combined with traditional video surveillance and access control, can help secure these facilities.
- Solar Farms – Theft at solar farms are also on the rise. Protecting solar farms is particularly challenging due to their remote locations. Thermal security cameras offer an ideal security solution as they can cover large areas effectively and function 24/7 in all weather conditions.
- Critical Infrastructure – Municipalities are particularly concerned with the security of critical infrastructure because lives depend on it. Thermal security cameras are now being widely deployed to protect facilities such as hospitals, airports, bridges, water towers, power stations, nuclear facilities, and more from vandalism and terrorist activities.
Choosing the Right Thermal Imaging Camera Isn’t Easy – Koorsen Can Help
The market for thermal imaging cameras in security applications has grown so quickly that businesses now have a wide range of thermal imaging systems to choose from, which can make selecting the right camera for your system challenging.
There are several factors that can affect both the quality and cost of a thermal security camera. And, different applications require cameras with specific features (e.g., wide-angle or telephoto lenses, different image qualities, etc.). It’s also important to select a camera that is compatible with your current security system to leverage its capabilities and enhance your overall security.
When investing in a thermal security camera, you can count on Koorsen to help you avoid making a costly mistake. Our security camera experts can help you determine the specific features you need for each of your applications so you can choose the best security cameras to fit both your budget and thermal imaging needs. Contact Koorsen today to learn more about how thermal security cameras can help you better protect your business.


